While opium may seldom be used in its purest form, many prescription medications either contain opium or are synthetically made to produce opium drug effects. Likewise, heroin, one of the most popular opium-derived drugs on the market, produces some of the strongest opium drug effects of all.
Opium contains certain alkaloids known for their ability to attach to specific opiate receptors in the brain and throughout the body. According to the Institute for Substance Abuse Treatment Evaluation, once activated, these receptors secrete unusually high levels of neurotransmitter chemicals, which slow down central nervous system processes.
With continued use, the resulting brain chemical imbalances take the form of uncomfortable opium drug effects. Opium-type drugs also produce a “high” that ultimately drives a person’s desire to keep using.
As one of the most addictive types of drugs on the market, identifying opium drug effects early on can help prevent unforeseen consequences down the road. Here are 10 opium drug effects to watch out for:
1. Constipation
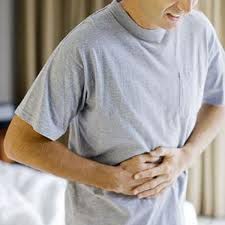
Opium causes constipation, nausea and more.
As central nervous system processes slow down, the body’s gastrointestinal functions also move slower. According to Northwestern University, constipation problems develop from slowed metabolism rates as well as a decrease in activity along the gastrointestinal tract.
2. Nausea and Vomiting
Impaired metabolism functions affect stomach activity as well as the chemicals processes involved with breaking down food. Opium users will likely lose their appetite as these symptoms persist.
3. Sedation
Sedation remains an across the board opium drug effect regardless of the type of drug involved. Opium naturally causes an increase in brain endorphin secretions, which depresses the body’s state of arousal.
4. Body Temperature Changes
Brain chemical balances interfere with the brain’s ability to regulate body temperature. Both chills and sweats develop as the brain attempts to restore some form of chemical equilibrium.
5. Increased Tolerance Levels
Brain cell receptors become less sensitive to opium’s effects with each successive dose. As a result, larger doses of the drug must be ingested to produce the same desired “high” effect.
6. Brain Damage
As tolerance levels increase, brain cell functions and brain cell structures weaken over time. With long-term opium use, damage to the brain can become permanent, impairing a person’s overall cognitive, emotional and motor functions.
7. Muscle Aches & Pains
Opium directly interferes with pain signaling processes throughout the central nervous system. Once chemical imbalances develop, opium drug effects take the form of muscle aches and pains throughout the body.
8. Muscle Spasms
Opium’s effects on motor coordination functions can cause muscle spasms in any area of the body, but mostly in the extremities. This condition can result in serious nerve damage with continued drug use.
9. Fatigue
Slowed metabolism processes impair the body’s ability to digest needed food nutrients. This in turn affects the amount of energy a person has. Feelings of fatigue will persist for as long as a person keeps using.
10. Addiction
With long-term drug use, both the body and mind become dependent on opium drug effects. At this point, users start to believe they “need” the drug to cope with everyday life.
 What Addiction Treatment Options Can Help With Opioid Withdrawal Symptoms? -
Withdrawal is often the first thing a person encounters during their treatment for addiction. According to the NIDA, the first stage in addiction treatment involves detoxification where the drug leaves the body and triggers withdrawal symptoms. With opioid addiction treatment, there are options available to help with the withdrawal symptoms. When you call to learn ...
What Addiction Treatment Options Can Help With Opioid Withdrawal Symptoms? -
Withdrawal is often the first thing a person encounters during their treatment for addiction. According to the NIDA, the first stage in addiction treatment involves detoxification where the drug leaves the body and triggers withdrawal symptoms. With opioid addiction treatment, there are options available to help with the withdrawal symptoms. When you call to learn ...  History of Opium -
The history of opium goes back to ancient times when the drug was used for ritual purposes and for anesthesia. The ancient Egyptians, Indians, and Romans used opium as a pain reliever and often included the drug in surgical procedures to keep pain at bay. The drug is even mentioned in medical texts from the ...
History of Opium -
The history of opium goes back to ancient times when the drug was used for ritual purposes and for anesthesia. The ancient Egyptians, Indians, and Romans used opium as a pain reliever and often included the drug in surgical procedures to keep pain at bay. The drug is even mentioned in medical texts from the ...  Opium Withdrawal Treatment Options -
The opium poppy, Papaver somniferum, is the source from which many narcotics including morphine, opium, codeine, and heroin are extracted. Opium is a highly addictive non-synthetic narcotic. “The intensity of opium’s euphoric effects on the brain depends on the dose and route of administration. It works quickly when smoked because the opiate chemicals pass into ...
Opium Withdrawal Treatment Options -
The opium poppy, Papaver somniferum, is the source from which many narcotics including morphine, opium, codeine, and heroin are extracted. Opium is a highly addictive non-synthetic narcotic. “The intensity of opium’s euphoric effects on the brain depends on the dose and route of administration. It works quickly when smoked because the opiate chemicals pass into ...  The Dangers of Opium Overdose Effects -
There are five main categories in drug classification based on their chemical ingredients and their effects on users. Opiates and opioids are one of the classified drug categories. These are highly addictive, non-synthetic narcotics that are extracted from the poppy plant, Papaver somniferum. Examples of opiates: heroin and morphine Examples of opioids: Demerol, Darvon and ...
The Dangers of Opium Overdose Effects -
There are five main categories in drug classification based on their chemical ingredients and their effects on users. Opiates and opioids are one of the classified drug categories. These are highly addictive, non-synthetic narcotics that are extracted from the poppy plant, Papaver somniferum. Examples of opiates: heroin and morphine Examples of opioids: Demerol, Darvon and ...  Opiate Addiction Help for Loved Ones -
If your loved one suffers from opiate addiction, there are resources available to help you and others affected through this difficult time.
Opiate Addiction Help for Loved Ones -
If your loved one suffers from opiate addiction, there are resources available to help you and others affected through this difficult time.